While solar energy technology is becoming more popular every day, it still faces several challenges. First, it is only available when the sun is shining, and this causes energy production to be intermittent, especially at night or on overcast days. Secondly, energy storage is crucial to avoid the energy shortages that may occur. Fortunately, there are several ways to store energy efficiently and at low cost. And with recent discoveries, such as floatovoltaics, these challenges may be solved in the future.
Today, silicon solar cells produce a low efficiency of around 26.7%, but they are also quite heavy. Despite their low efficiency, they are still used in industrial applications. Newer developments include multi-layer solar junctions, or “tandem cells,” which consist of two or more subcells connected by interconnecting layers. Although they are slower than other multi-junctions, they are still a significant advancement over the traditional silicon cells.
The solar cell is the key to converting sunlight into energy. The semiconductors in each solar cell absorb light and loosen electrons in atoms. When these loose electrons are collected in the semiconductor, an electrical field is created, which directs them into an electric current. This current flows in one direction and then flows through a wire, where it is converted to AC power.
Since 1954, silicon-based cells have dominated the solar market. But recent breakthroughs have led to the development of new materials based on perovskite. These materials have special crystal structures, making them more efficient than silicon. They can also be made transparent and flexible. These new materials are expected to lower the costs of solar power. These advances should help make solar power a reality for every home and business owner. However, they are still years away from commercialization.
In 1894, the first solar cell was developed by Aleksandr Stoletov. This cell was the first example of solar energy technology. It used the photoelectric effect – when light hits a material, it releases electrons. It was later discovered that ultraviolet light created more power than light. This effect was further explored by scientists, including Heinrich Hertz, who found that sunlight has an ultraviolet wavelength. These scientists discovered that the photoelectric effect is what enables solar cells to generate electricity.
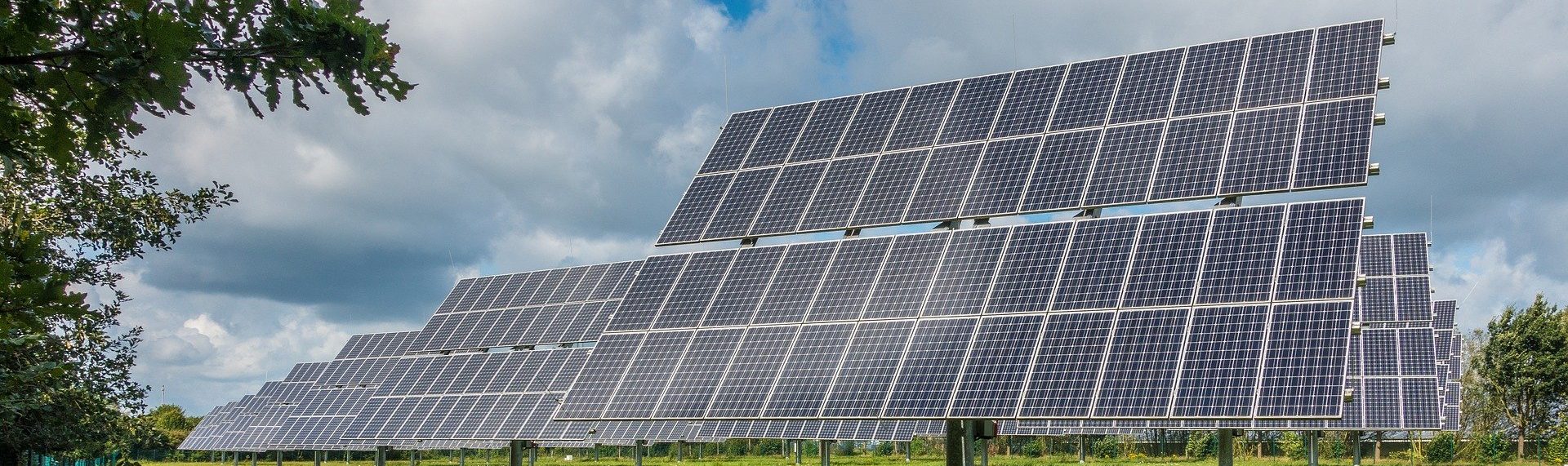
For example, solar panels are vulnerable to extreme weather conditions. These extreme events can lead to damage to the fine glass surfaces of solar panels. To reduce this problem, solar power plants use metal grills to protect the cells from damaging weather events. These metal grills allow a high percentage of sunlight to enter the panels while keeping them protected.
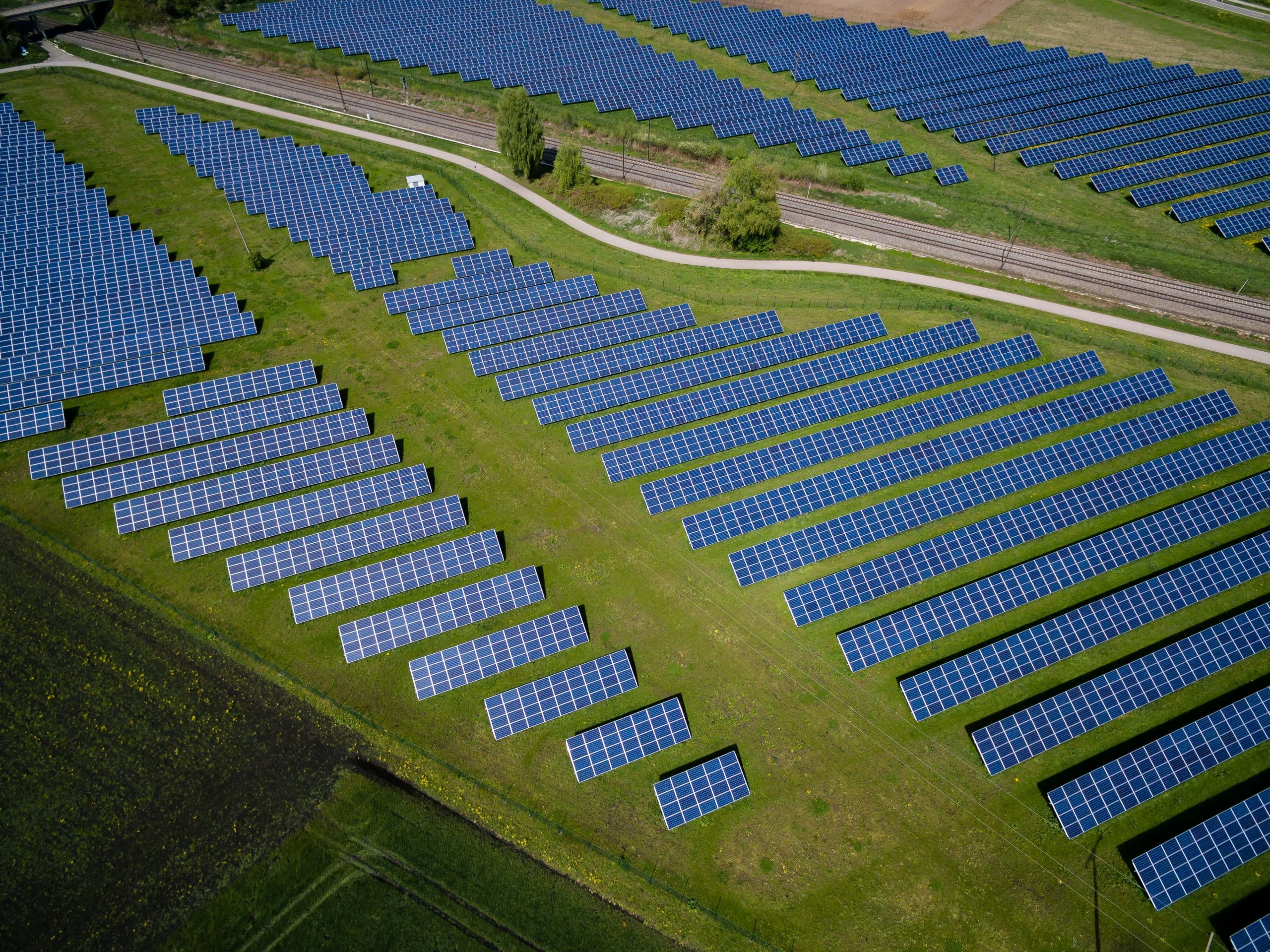
Concentrated solar-thermal power systems make use of mirrors and lenses to focus the sun’s light. The resulting heat is converted into electricity and stored for later use. These systems are often large, and they must be integrated into existing electrical grids. In addition to converting light into electricity, solar panels can also provide heat, light, and cooling for a home.