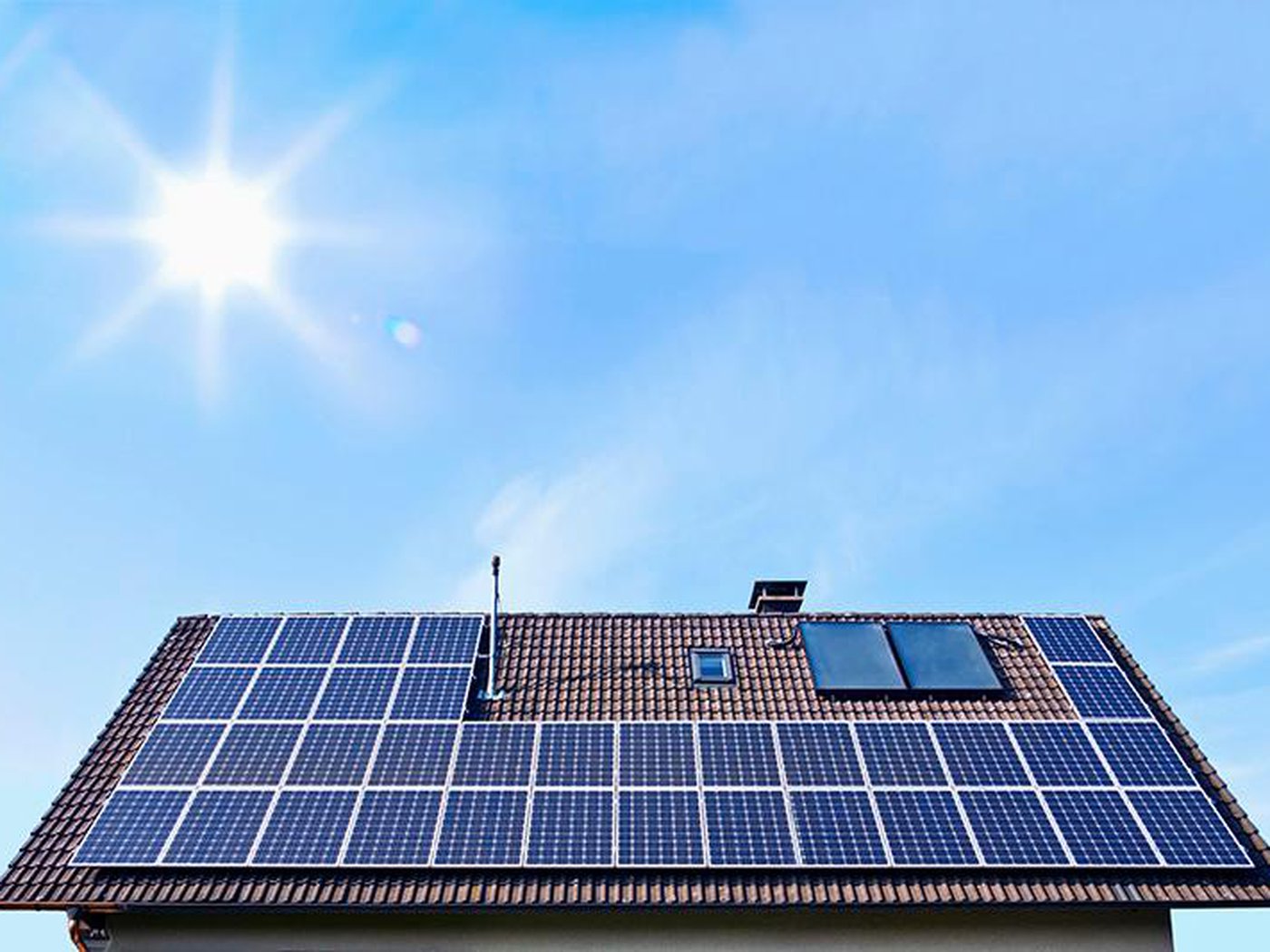
Using more solar power is important to our planet. However, there is one major problem. Solar power is expensive to install and maintain. This cost is the primary reason why many people choose to use other forms of power. Wind and water power are much cheaper to use. In addition, they are less harmful to the environment than solar panels.
Cost of installing and maintaining
Getting your solar power system installed can be expensive. It’s not only the cost of the panels, but the mounting infrastructure, cabling, and other components. It can also be expensive to remove and reinstall your solar panels.
While most solar panel systems require little maintenance, you may need to pay for a professional inspection every now and then. It’s also possible to buy a maintenance package. Most of these packages include cleaning, inspection, and pest control measures.
If you live in an area with a lot of bird activity, you may want to consider installing bird mesh. This will keep birds from nesting beneath your solar panels, which can block their ability to absorb sunlight. You may also want to consider installing snow guards, which can protect your panels from heavy snowfall.
You may also want to consider purchasing a warranty. Most solar panels are guaranteed to operate for a certain amount of time. They may also qualify for rebates or tax incentives, which can offset some of the cost.
Access to solar power hasn’t been equitable
Despite the rapid growth of solar power, access to solar power has not been equitable to all. While the number of households using solar has increased dramatically, low-income households have had to wait longer to adopt solar. As a result, low-income households have paid a disproportionate amount of money towards energy bills. The high energy burden is correlated with stress and an increased risk of respiratory diseases.
One way to increase solar adoption is through financial incentives. Tax breaks and rebates can make solar more appealing to lower-income households. However, these incentives can also aggravate the solar divide.
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) is currently proposing to create a $600 million fund to help underrepresented communities get access to solar panels. The proposal could be voted on as early as January 27th. The California Solar & Storage Association is one of 600 coalitions fighting against the proposal. Several other environmental advocates are supporting the proposal.
Wind energy is less harmful to the environment than solar panels
Compared to other renewable energy technologies, wind energy is a clean fuel source that does not produce greenhouse gas emissions. However, wind power is still less environmentally friendly than solar power.
Wind energy is a source of electricity that harnesses the power of wind, which is caused by the rotation of the Earth. Wind energy also does not produce pollutants, such as carbon dioxide or sulfur dioxide.
There is no reason why wind energy should not be used on a larger scale than solar power. Wind energy is one of the fastest growing energy sources in the world.
The most notable environmental effect of wind power is the warming effect it has on the local area it is in. Large-scale wind farms could become active players in the climate system. They can warm average surface temperatures over the continental U.S. by 0.24 degrees Celsius.
Another noteworthy benefit of wind is that it can operate without fuel. This is important because fossil fuel power plants emit pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. The pollutants from these power plants are not good for human health, and they also have economic consequences.
Regionally unequal transition of electricity generated from coal and fossil fuels
Using a spatially explicit electricity system model, the IEA has identified a regionally unequal transition of electricity generated from coal and fossil fuels. This is an important topic for policymakers, given that the transition to a clean energy economy is a key issue for many communities. However, there are few studies that have examined the regional impacts of electricity sector transitions. IEA work is responding to governments’ demands for deeper insights into energy employment, while also building on the ILO’s Green Jobs program. The results of the analysis will inform policy makers and help them to understand clean energy transition scenarios.
The results demonstrate that the regional impacts of electricity sector transitions are mostly driven by changes in generation capacities of a few technologies. These are often associated with cost efficiency. However, there is also a complex network of factors that determines fuel choice. These factors include the preferences of the host countries, which determine technology quality. Depending on the host country, these preferences determine the overall mix of fuel types and their distribution among regions.